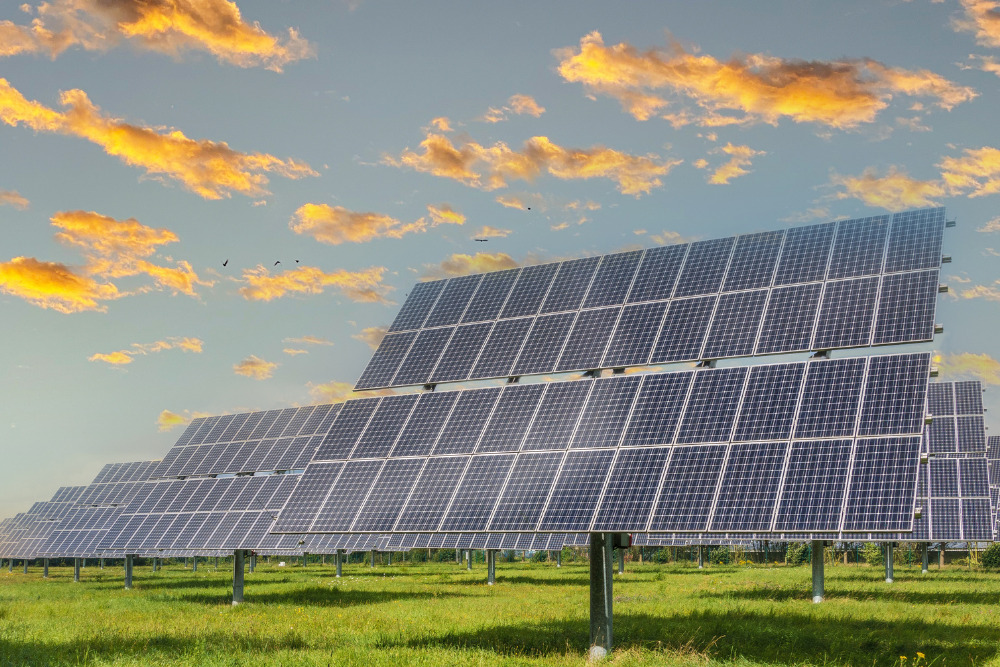
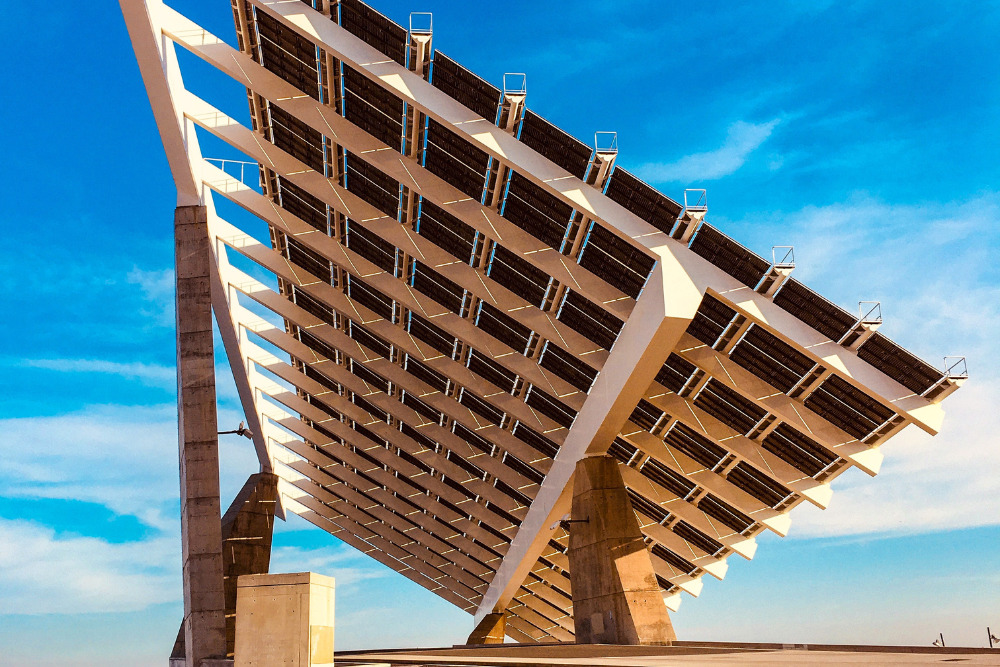
As the name implies, bifacial solar panels are two-sided; they capture sun power and generate energy from both sides. Bifacial solar panels are more effective than traditional solar modules and best for high energy needs.
Bifacial solar cells work like standard solar cells by harnessing solar power and converting it into renewable energy. However, unlike the monofacial panels, these modules have solar cells on both sides and lack a back sheet for maximum sunlight absorption. Their rear side absorbs reflected light off the ground or the surface it faces.
This technology requires a reflective surface on the back to maximize light absorption from both sides, so there must be space between the panel and the surface where it's installed.
Reflective surfaces include water, sandy or stony ground, or glass. For this reason, these modules are impractical for rooftops since it's impossible to absorb reflected light from both sides.
The best way to install these panels is to create awnings or canopies to enhance energy production from both sides of the panel. A solar pergola, carport, or gazebo roofing will also do the trick, especially for large installations.

Bifacial Vs. Monofacial Solar Panels
Bifacial and monofacial panels have significant differences based on their design. While they function the same in harnessing solar energy, their technology sets them apart. These differences include:
- Solar technology: Bifacial solar modules have solar cells on both sides, so they're frameless and lack a back sheet. On the other hand, monofacial panels have solar cells on one side, with a frame and back sheet.
- Installation: Bifacial panels can be installed vertically to enhance light absorption from both sides. When installed horizontally, there must be space between them to allow light absorption from the back of the panels. In contrast, monofacial panels are installed horizontally so that only the front side is exposed to the sun.
- Efficiency: Bifacial panels are more efficient than monofacial panels due to the unique double glass technology. Also, they have busbars on both sides to further enhance efficiency. Busbars are narrow, flat strips made from highly conductive materials like copper or silver. They are placed on the surface of solar cells to collect and transfer electrical current.
Pros & Cons Of Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels have many advantages due to their unique solar technology. But they also have a few disadvantages.
Pros
- More efficient: Bifacial panels are more efficient since they generate energy from both sides. The efficiencies are exceptionally high for monocrystalline cells and Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) bifacial panels.
- They take up less space: Due to their high efficiency, homeowners need fewer PV modules for home energy needs. Therefore, they take up less space than other monocrystalline and polycrystalline cells. Also, bifacial panels are usually installed vertically or at a tilted angle, thus requiring less space.
- They can withstand snowy climates: Bifacial panels are ideal even in snowy climates since they absorb light from the back side when the front side is covered with snow. They don't accumulate much snow when installed vertically or at a tilted angle.
- More durable: Bifacial panels are more durable thanks to their double-sided tempered glass. The lack of a frame is also one less component to potentially be damaged.
- Discourage pests: Because they're installed vertically or at steep angles, there's no space for pests such as birds and rodents, which can destroy the solar system.
Cons
- They're costly: The main downside of bifacial panels is their initial costs. These panels cost more than standard modules because of their unique technology. Also, their installation is more complicated, resulting in higher labor costs. However, users will achieve a faster return on investment since the panels produce more energy.
- Not practical for homeowners: Bifacial panels aren't ideal for home applications due to their high cost. While their efficiency is top-notch, the cost may not be worthwhile for home energy needs. Also, rooftop installation of these panels is complicated and further drives up the cost.
- Complex installation: Bifacial panels aren't ideal for conventional surfaces since they use special racking to maximize light absorption and power output. Also, they're heavier and difficult to handle, which increases labor costs.
Best Uses For Bifacial Solar Panels
- Ground-mounted solar farms: Bifacial panels are ideal for large-scale solar farms placed on open land or in solar fields where they can use trackers to increase energy production.
- Rooftop installations: Bifacial panels can be used on commercial or industrial rooftops, especially those with reflective surfaces like white or metal roofs. They can take advantage of both direct sunlight and reflected light to generate more electricity.
- Carports and solar canopies: Bifacial solar panels can be integrated into carports and solar canopies in parking lots. They panels serve dual purposes by providing shaded parking spaces while also generating electricity from sunlight and reflected light.
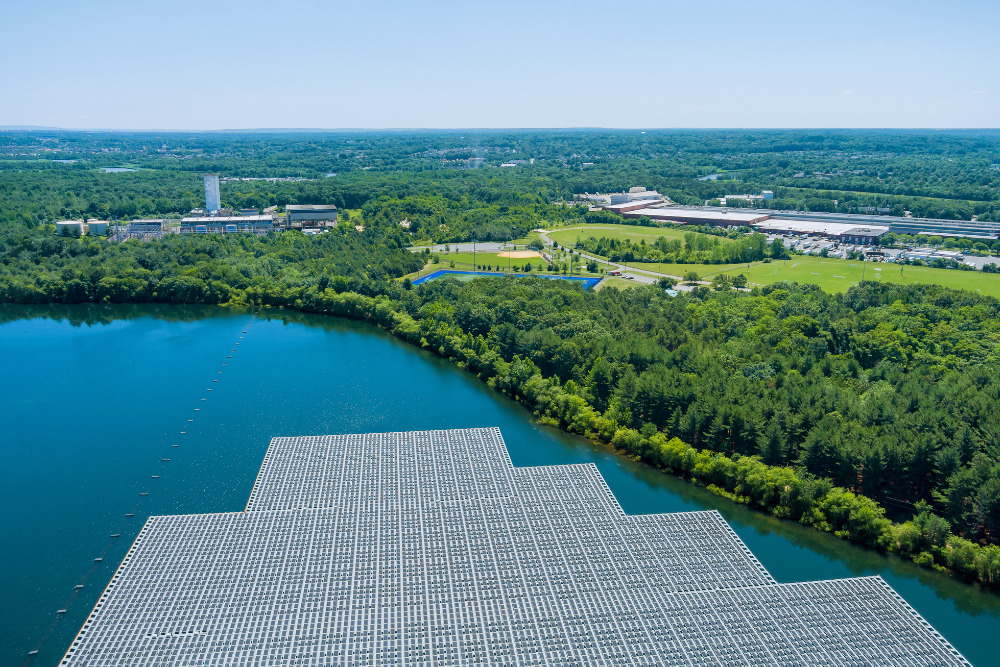
- Floating solar arrays: Bifacial panels are suitable for floating solar installations on bodies of water such as reservoirs, ponds, and lakes. The water's reflective surface enhances their energy capture.
- Agricultural applications: Bifacial panels can be installed on farms, above crops, or on the perimeters of fields.
- Urban environments: Bifacial panels can be used in urban settings where vertical surfaces, like noise barriers along highways or building facades, can benefit from the reflected sunlight to maximize energy production in limited space.
- Desert regions: In desert areas with high sunlight intensity and reflective surfaces like sand, bifacial solar panels are especially effective, as they can capture both direct sunlight and reflected light from the sand.
- Snowy climates: Bifacial panels can perform well in snowy regions, as the snow's reflectivity can enhance their energy generation during winter months.
- Portable and temporary installations: Bifacial panels can be used for temporary installations such as events, construction sites, disaster relief, or military deployments, where flexibility and energy efficiency are crucial.

Are Bifacial Solar Panels Worth It?
Bifacial PV panels are worth it for large solar panel installations, especially for high-consumption businesses or Independent Power Producers (IPPs) that run solar farms. Due to their high efficiency and durability, you'll get faster returns on investment.
According to a study by a leading solar panel manufacturer LONGI, bifacial panels combined with trackers produce 27% more energy than traditional solar panels, making these photovoltaic panels a game changer for large-scale and commercial users.