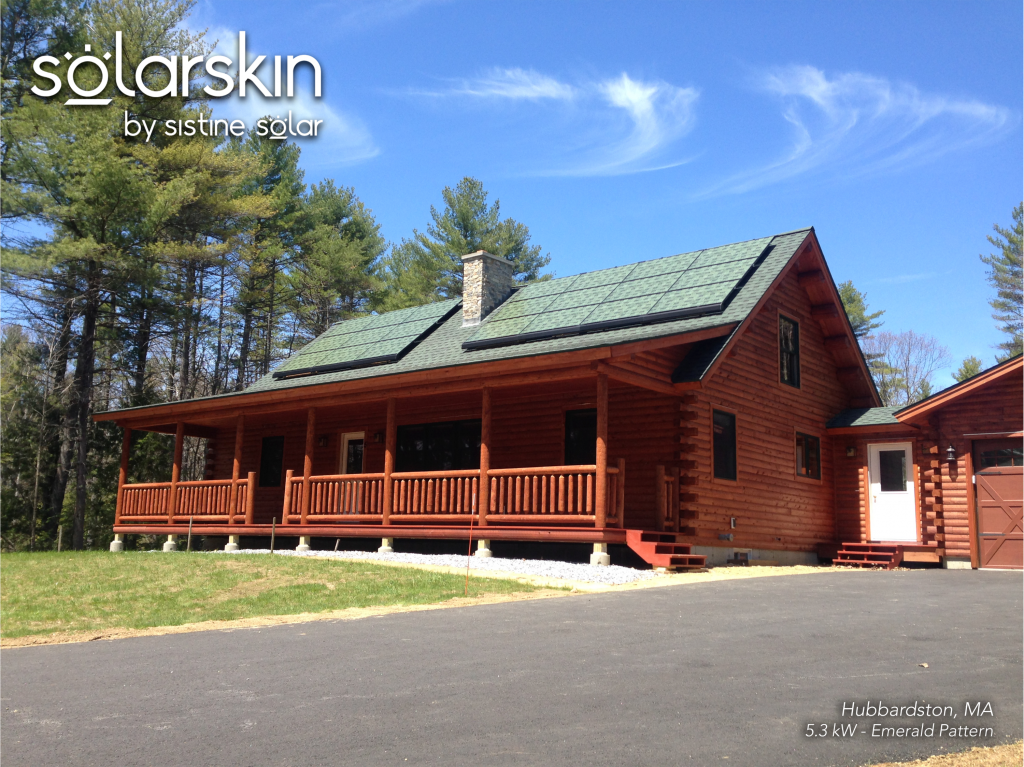
The cost of a residential solar energy system, including solar panel installation costs, typically ranges from $15,000 to $25,000, or $3-$5 per watt. Several factors affect the price, including system size, panel type, and geographic location.
As more homeowners seek sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions, the popularity of residential solar systems continues to soar. Harnessing the sun's power offers numerous benefits, from reducing utility bills to lowering your carbon footprint.
However, one crucial factor homeowners consider before switching to solar is the cost. Understanding the financial aspects of installing residential solar panels is essential for making informed decisions.
National Average For Solar Panels In 2023
The national average cost of solar panels in the United States in 2023 is $20,650 after considering the federal solar tax credit.
On a cost-per-watt ($/W) basis, solar panel prices in 2023 average $2.95/W (before incentives) with a range of $3-$5 per watt.
The cost of solar panels has been declining in recent years. In 2010, the average cost of a solar system was $30,000. Today, the average price is $20,650. This decline in cost is due to many factors, including:
- Improved technology
- Increased competition
- Government incentives
How Is The Cost Of Solar Determined?
Solar panel installation costs depend on several factors, including:
- The size of the solar system
- The type of solar panels
- The location of the home
- The cost of labor
- The availability of incentives
System Size
The higher your energy needs, the more panels you’ll need if you want to significantly reduce or eliminate your electricity bill.
Panel Type
Different types of solar panels are available, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels. Monocrystalline panels are more efficient but cost more, while polycrystalline panels offer a slightly lower price point.
Thin-film panels are less common for residential installations.
Location
Your location will also dictate the system size. For example, a 5kW solar system in Arizona or California will cost less than a 5kW solar system in Idaho. This is because these states have more sunshine, making the solar panels more efficient. Simply put, you’ll need more panels to produce the same amount of energy in Idaho.
Labor
Labor costs vary drastically by state, and are generally higher in urban areas than in rural ones.
Incentives
The overall cost is also significantly reduced through tax incentives, such as the government's Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC). The ITC federal solar tax credit allows homeowners to deduct 30% of the solar system costs from their federal taxes, making solar more affordable.
Many state and local incentives are also available.
How Long Does It Take To Break Even On Solar Panels?
Solar panel systems can pay for themselves in 6-9 years.
The payback period for solar panels varies based on several factors, including:
- Initial cost of the system
- Rebates
- Energy consumption
- Local electricity rates
- Financing options
- Incentives available from the federal government and local utility companies
The payback period reflects the "return on investment" (ROI) or the time it takes to recoup the initial investment through energy savings. The ROI is determined by comparing the cost of purchasing and installing the solar panels to how much money you save on the cost of electricity over time.
To estimate the payback period for your specific situation, you'll need to consider the following:
- Calculate the total cost of purchasing and installing the solar panel system, including equipment, installation, permits, and additional expenses.
- Evaluate your average monthly electricity consumption and the potential energy production of the solar panel system. This information will help estimate how much you save on electricity bills (or eliminate your bill altogether).
- Research available incentives, such as federal or local tax credits, rebates, or net metering programs. These incentives significantly reduces the upfront cost and shorten the payback period.
- Consider whether you will purchase the solar panel system outright, finance it through a loan, or lease it. Different financing options affect the payback period and overall financial benefits.
How Much Electricity Does A Solar Panel Produce?
electricity per hour (0.25 to 0.40 kilowatt-hours).
However, the actual output depends on specific environmental conditions and the characteristics of the panel itself.
How much electricity a solar panel produces depends on several key factors, such as its positioning and exposure to sunlight, the panel's wattage, and the efficiency of its photovoltaic cells. These elements collectively determine the amount of electricity generated.
How Many Solar Panels Are Needed For An Average 2,000 Square Foot Home?
As a general guideline, a 6 kW system is typically sufficient to meet the power demands of an average-sized home. This is approximately 20 solar panels.
However, conducting a detailed energy analysis is essential to make an accurate assessment of your household's electricity usage and determine the optimal system size. Factors such as geographical location, available sunlight, energy efficiency measures, and individual lifestyle choices also influence the number of solar panels needed to power a 2,000-square-foot home.
How To Pay For A Solar Power System
There are many financing avenues to explore if you want to go solar. Researching options such as solar loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) will help you choose the best option for your needs and budget.
In addition to financing options, you can find a range of incentives to encourage homeowners to adopt solar power. These incentives encompass investment tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs. Investment tax credits significantly reduce your overall income tax liability, lessening the financial burden of installing solar panels.
Rebates offer upfront cost reductions, making the initial investment more affordable. Net metering enables you to sell any surplus electricity your solar system generates back to the utility company, potentially resulting in further savings.
Solar companies, solar energy professionals, or financial experts will help you maximize the benefits of going solar and navigate the complexities of financing such an operation.
Do Solar Panels Reduce A Home's Energy Consumption?
Solar panels can reduce a home's energy consumption, often by as much as 100%. If your solar panels generate enough electricity, you can reduce your reliance on traditional utility power and potentially eliminate your electric bill entirely.
By utilizing the power of the sun and converting it into clean, renewable energy, solar panels offer the opportunity to achieve energy independence and reduce your environmental impact while enjoying the financial benefits of lower or even zero energy costs.
Is Solar A Good Investment?
Solar energy investment offers a compelling opportunity for homeowners, as it yields a favorable return on investment over time. By transitioning to solar power, you benefit from substantial energy bill savings while enhancing your home value.
However, you should also consider the warranty and reputation of the installation company when evaluating solar providers. Reputable companies often offer warranties on both the panels and the installation work, ensuring that homeowners are protected in case of any issues.
One popular option for homeowners is a solar lease, where a third-party provider installs and maintains the solar panels. In this arrangement, homeowners enjoy the benefits of solar energy without upfront costs, as they pay a fixed monthly amount to the leasing company. However, it's worth noting that with a solar lease, homeowners may not be eligible for certain solar incentives, like the ITC.
You also have to consider the upfront costs, electricity savings, and available incentives to determine the break-even point of your specific solar investment. Factors like the size of the system and local electricity costs play a significant role in determining the payback period.
With the availability of federal and state incentives, the initial cost of installing solar panels has become increasingly affordable, making it an attractive option for those seeking to embrace clean and renewable energy sources.
Homeowners can significantly reduce or eliminate their monthly electricity bills by generating clean energy from the sun, especially in areas with high electricity costs, like Arizona. The amount of energy a solar power system produces offsets a substantial portion of the energy usage, leading to lower monthly payments to the utility company.