Being the most popular renewable energy source, global governments have invested in research and development to reduce costs, improve technology, increase efficiency, and ultimately expand the adoption of solar.
Why Is Solar R&D Important?
Solar research and development (R&D) is critically important for several reasons, including advancing technology, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and addressing environmental and energy challenges.
- Lower costs: One of the primary goals of solar R&D is to reduce the cost of solar energy technologies. Lower costs make solar power more affordable and competitive with fossil fuels, which accelerates its adoption and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. As the cost of solar panels, inverters and other components decreases, more people and businesses can afford to install solar systems.
- Increase efficiency: R&D efforts aim to improve the efficiency of solar panels and other solar technologies. Higher efficiency means that solar panels can convert more sunlight into electricity, which minimizes the number of panels and installation space needed. Improved efficiency also means that solar installations can perform well in areas with less sunlight.
- Identify gaps in end-of-life solar panels: Currently, more than 90% of solar panels find their way into landfills, leading to the loss of valuable materials and negatively impacting the environment. R&D is the only way to deal with old panels by exploring better and cheaper recycling processes to reduce dumping.
- Advance solar cell technology: Ongoing R&D leads to technological breakthroughs and innovations in the field of solar energy. This includes the development of new materials, manufacturing processes, and designs that enhance the performance and durability of solar panels. Advanced technologies such as bifacial solar panels, tandem solar cells, and perovskite solar cells have emerged from R&D efforts.
- Identify and mitigate environment impacts: While solar panels produce clean energy, they still contribute to carbon emissions during their life cycle. Also, the construction of solar farms can impact wildlife without careful planning. Therefore, solar R&D is essential in unearthing the negative impacts of solar energy and developing sustainable mitigation strategies.
- Add jobs and support economic growth: The solar industry has the potential to create a significant number of jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research. R&D investments can stimulate economic growth by supporting a skilled workforce.
- Support better grid integration: Solar R&D can contribute to the development of grid integration technologies, such as energy storage systems and smart grids. These innovations help manage the intermittent nature of solar energy and make it more reliable and compatible with existing infrastructure.
- Transition to clean energy on a global level: Solar energy plays a crucial role in the transition to a more sustainable future. Solar R&D can help countries and regions reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and meet their renewable energy goals.
- Provide better access to electricity: Solar technology advancements can make it easier to provide electricity to remote and underserved areas. Off-grid and microgrid solutions powered by solar energy can improve energy access and quality of life for people in these areas.

Who Conducts Solar Research & Development?
Solar research and development is a broad area requiring intense funding and knowledge. Therefore, different stakeholders are involved, each with a different mandate. They include governmental and nongovernmental organizations, such as:
- Government Agencies: Government agencies in many countries allocate funding and resources for solar R&D. In the United States, the Department of Energy's (DOE) Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) plays a significant role in funding and coordinating solar research initiatives through programs like the SunShot Initiative and the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E).
- Research Universities and Academic Institutions: Universities and research institutions around the world conduct research on solar energy. They often collaborate with government agencies and private companies to develop new materials, technologies, and methods related to solar energy.
- National Laboratories: National laboratories, such as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the United States, specialize in renewable energy research and development. They work on various aspects of solar energy, including materials science, photovoltaics, and grid integration.
- Private Companies: Many private companies, both large and small, are involved in solar R&D. These companies include solar panel manufacturers, solar technology startups, energy storage companies, and firms specializing in related technologies like inverters and solar tracking systems. They invest in R&D to improve their products and gain a competitive edge.
- Industry Associations: Industry and trade associations, such as the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) in the United States, often support and fund R&D initiatives. They advocate for policies that promote solar energy and collaborate on research projects.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofit organizations, like the Solar Foundation and the Solar Energy Research Institute for India and the United States (SERIIUS), focus on advancing solar technology and promoting widespread adoption. They may conduct research or partner with other organizations to fund R&D projects.
- International Collaborations: Solar R&D frequently involves international collaborations. Countries and regions may work together on joint research projects to pool resources and expertise, share data, and expand progress in solar technology.
- Startups: Entrepreneurial ventures and startup companies often focus on innovative solar technologies. Incubators and accelerators may provide funding, mentorship, and resources to support these startups in their R&D efforts.
- Financial Institutions: Some financial institutions and investors fund R&D projects related to solar energy as they recognize the long-term potential for returns on investment in clean energy technologies.
- Utilities and Energy Companies: Utilities and large energy companies often invest in solar R&D to develop new ways of integrating solar power into their grids.
- International Organizations: Entities like the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and the International Energy Agency (IEA) support global efforts in renewable energy research and development, including solar energy.

How Is Solar Research & Development Funded?
The U.S. Department of Energy Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) is one of the primary funding sources for solar research and development. It runs an open competitive solicitation process where researchers can apply.
Researchers can apply as individuals or collaborative groups to receive funds and support for energy innovation projects. The funding is available for solar-related research areas like energy development and the advancement of solar solutions.
The application process may take months due to its competitiveness, and once the results are out, SETO invites successful applicants for a negotiation of the cooperative agreement.
Outside of SETO, solar research is funded by the entity conducting it, such as an industry organization, academic institution, or private investor.
What Research Areas Are Specific To Solar Panels?
Solar research and development is a broad scope, but here are specific areas for solar panels.
- Solar cell technology research covering various aspects, such as using cheaper silicon alternatives to reduce the cost of solar.
- Efficiency research covers improving solar module efficiency to boost energy generation and increase solar use.
- Inverter research focuses on enhancing inverters' reliability to reduce failures in the system.
- Energy storage/batteries research aims to develop better storage systems with enough backup power.
What New Technology Has Emerged From Solar R&D?
As solar energy research and development continues, there are numerous groundbreaking advancements as a result. These include:
- Perovskite: This is a fully rollable and printable solar cell.
- Thin-film solar: Lightweight and flexible panels offering portable power solutions.
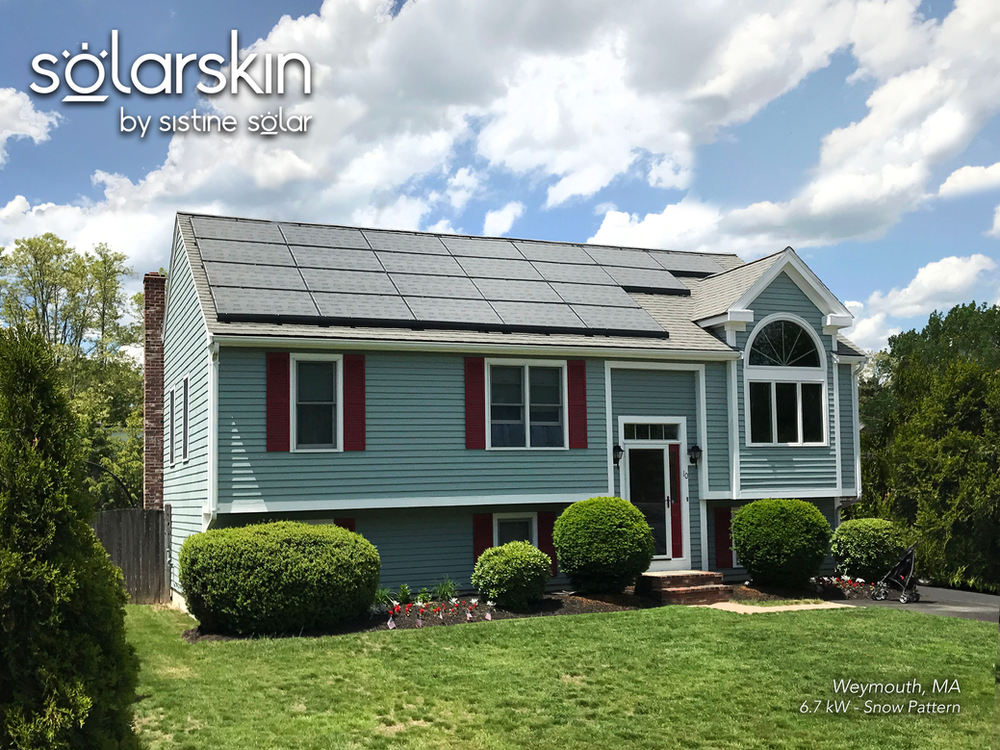
- SolarSkin: A new technology that uses custom-printed overlays to change the aesthetics of solar panels. For homeowners, this usually means making their solar panels match their roof's tiles or shingles. Businesses often use SolarSkin to turn their large solar arrays into a giant branding opportunity.
- Quantum dot solar cells: The cells use quantum dot material allowing the panels to absorb light of varying spectra to enhance energy efficiency.
- Back contact (IBC) cells: They utilize the back of the panel for contacts, leaving the front specifically for light absorption.