Traditional thermoelectric power plants use a lot of water for cooling. Conversely, solar panels can help conserve water once operational, making them a long-term water-saving solution.
How Much Water Do Solar Panels Use?
The only time solar panels use water is during the manufacturing and maintenance processes. Otherwise, they do not use any water. Because they do not require any water to generate electricity, they are far more sustainable than traditional power plants, which use more than 10,000 gallons of water per megawatt of electricity generated.
During Manufacturing
Solar panels use large amounts of semiconductors, usually silicon, which requires the use of a lot of water during the manufacturing process. Just a 2-foot wide area of semiconductors uses 4,400 gallons of water during manufacturing, and large semiconductor factories use millions of gallons of water per day. Large solar arrays use hundreds of square feet of semiconductors, so there is quite a lot of water usage during the manufacturing process.
However, there are more sustainable solar panel manufacturers that may use methods to cut down on water use. For examples, Trina Solar is considered to have the most sustainable business practices and manufacturing processes among solar brands. From 2020 to 2021, they reduced water consumption in their solar manufacturing processes by 46%.
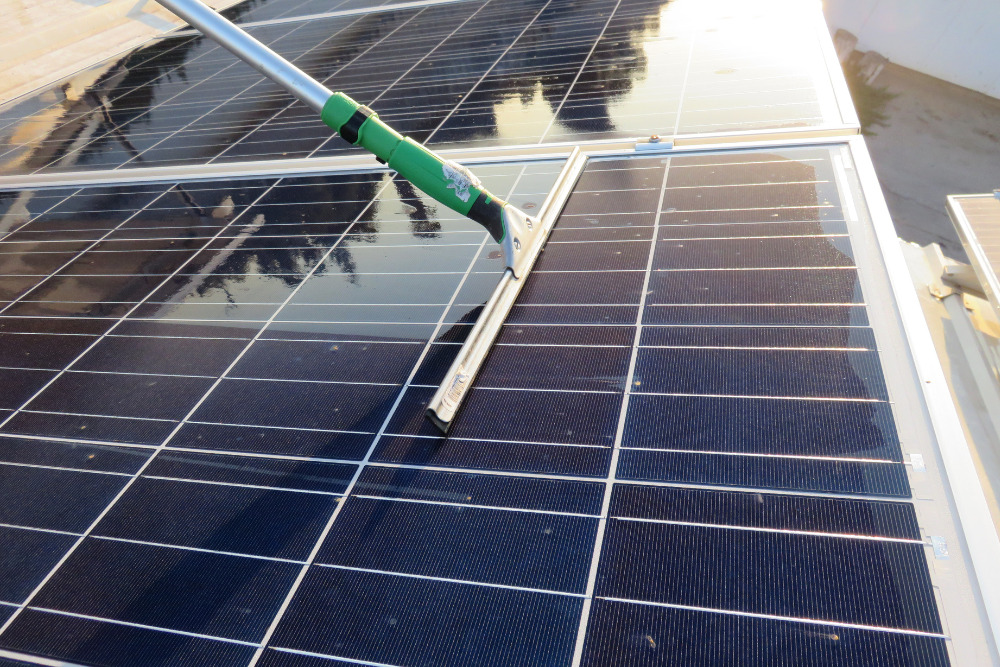
During Cleaning
Once your solar energy panels are up and running, your renewable energy will come from the sun itself, so the only time you will use water for your solar panels is when you have to clean them. As a general rule, they should be cleaned once or twice a year to maintain efficiency and performance.
However, there are ways to use less water when cleaning your panels. Simply being aware of how much water you are using is a good first step. Turn off the hose except when you need it or fill a bucket to control water consumption.

How Solar Panels Conserve Water
There are several ways solar panels conserve water. Some of these include:
- Not using water during operation. Unlike power plants, solar power plants do not require water to obtain electric power. Power plants require water for their cooling systems (also known as wet cooling), but solar panels have dry cooling, meaning they do not need water. According to Duke Power, a household may save up to 16,200 gallons of water per year on average by installing a rooftop solar system and not using as much traditional power sources. In some other states, such as California, the savings can increase to 53,000 gallons per year. That is equivalent to 60% of the average water usage in households in the U.S. Though you will not see these savings on your water bill, they are still extremely important.
- Conserving aquatic ecosystems and water resources. Unlike many other energy sources, solar power output does not require the extraction of water from rivers, lakes, groundwater sources, and other natural water sources. Therefore, it preserves the biodiversity of wildlife and plants, keeping your water footprint down and increasing sustainability.
- Reducing waste and pollution. Thermal power plants, nuclear power plants, and several other energy sources can create large-scale waste and pollution, leaving water sources contaminated. Solar projects can help to reduce and even eliminate waste during energy production.
- Floating solar helps minimize evaporation. Floating photovoltaics (FPV), or floating solar installations optimize land use by utilizing large bodies of water. These large arrays provide protection for marine and minimize evaporation to further conserve water.
- Water management and indirect conservation help with water emissions. Fracking and mining for fossil fuels, such as natural gas, for electricity generation use an exorbitant amount of water. Because these are finite resources, it causes a never-ending cycle of using resources to make more resources. Solar PV creates clean energy from renewable resources, which creates sustainability. There is no water used in this technique, except during cleaning.