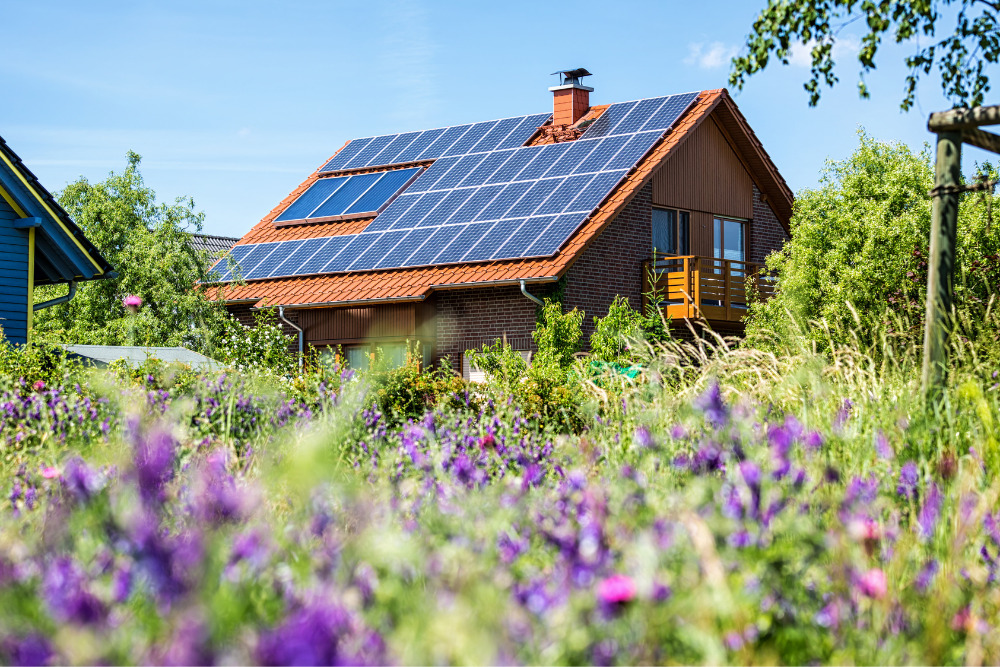
Residential solar panels work through absorption of sunlight. The cells in the panel use the photons from the sunpower to create an electric field across the layers which produces electricity. This electricity can be used immediately or can be stored in solar batteries.
Using solar power instead of conventional forms of energy reduces the amount of carbon and other pollutants that are released into the environment. Not only do solar panels produce clean energy and improve air quality, they also help homeowners save money on their energy bills.
How Does Solar Technology Work?
Solar technology works by converting the sun’s energy into electricity through the use of photovoltaic (PV) cells.
These cells are composed of semiconductor materials, usually silicon, that absorb photons from the sun’s rays. They then release electrons, which generate a direct current (DC) of electricity. Home appliances are designed to use alternating current (AC) electricity, so the DC power generated by the solar cells needs to be converted by a solar inverter before it’s supplied to the home.
The inverter will then feed AC power to the home's circuit breaker panel and then the power is available to service any electrical loads within your property. Often times, solar panels produce more solar power than your energy needs. In areas where net metering is available, the excess energy can flow back to the local utility grid and "sold" for credits on your future electricity bills.
Alternatively, you can store excess energy generated during the day in a solar battery for future use. Depending on your energy use, solar system, and battery size, you may be able to completely cut ties with the electricity company. At the very least, you'll have a backup energy source for night time or when the sun isn't shining.
Although solar technology has been around since the 1800s, it has only recently become a feasible option for average homeowners. The two biggest factors that have made it more accessible are the lower cost of solar panels and the improvements in the efficiency of solar cells.
How To Know If Solar Panels Are Suitable For Your Home
When deciding if solar panels are right for your home, you should consider the amount of sunlight your home receives, the size of your home, and your energy usage.
Solar energy functions in a broad range of climates, from rainy areas to places with extreme heat. Solar panels work best with direct sunlight, but high-efficiency solar panels can convert direct or indirect sunlight into electricity. This allows them to produce energy even on a cloudy day. If you live in an area with extreme weather conditions, be sure to choose panels with high durability ratings.
The size of your home is another important factor as larger homes will use more electricity than smaller ones. Before considering installing solar panels, you should also analyze your monthly energy costs. If you don’t usually have a high electricity bill or one that goes over $75 through the year, it may not be worth installing solar panels. A solar installation company can visit your home to provide you with accurate information on your home’s compatibility with solar panels.

How Much Solar Electricity Will Your Home Generate?
The amount of solar electricity your home will generate depends on the amount of sunlight your home receives and the efficiency of your solar panels.
The amount of sunlight that hits a solar panel is the biggest factor in how much electricity it will generate. Overhanging tree branches or chimneys that cast shadows on the panels can reduce your panels’ production. Solar panels will also be able to generate more electricity in places that get more peak sun hours.
The type of solar panel you use also affects how much energy it can produce. Most solar panels are made of monocrystalline solar cells, which are the most efficient solar cells today. A polycrystalline solar panel is slightly less efficient, but also more affordable. The caveat is that a house with high energy needs would need more polycrystalline panels to produce the same amount of electricity, thus more roof space for installation. The average solar panel is able to output between 370 and 400 watts of power, which is about 2 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per day.
What Is The Cost Of A Residential Solar Panel System?
The national average cost for a solar panel system in 2023 is around $3-$5 pet watt.
This means a 6 kw system would cost around $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives. However, the cost of solar panels can vary depending on the size of the system, installation costs, and the type of solar panels used. Solar panel costs have been falling in recent years, making them more affordable for homeowners.
What Is Net Metering?
Net metering is a program that allows homeowners to sell excess electricity back to their electric company.
In net-metered homes, excess solar power generated is sent back to the grid for credit on future electricity bills. Homeowners only pay their net energy use, or the difference between how much grid energy they used minus solar energy sold.
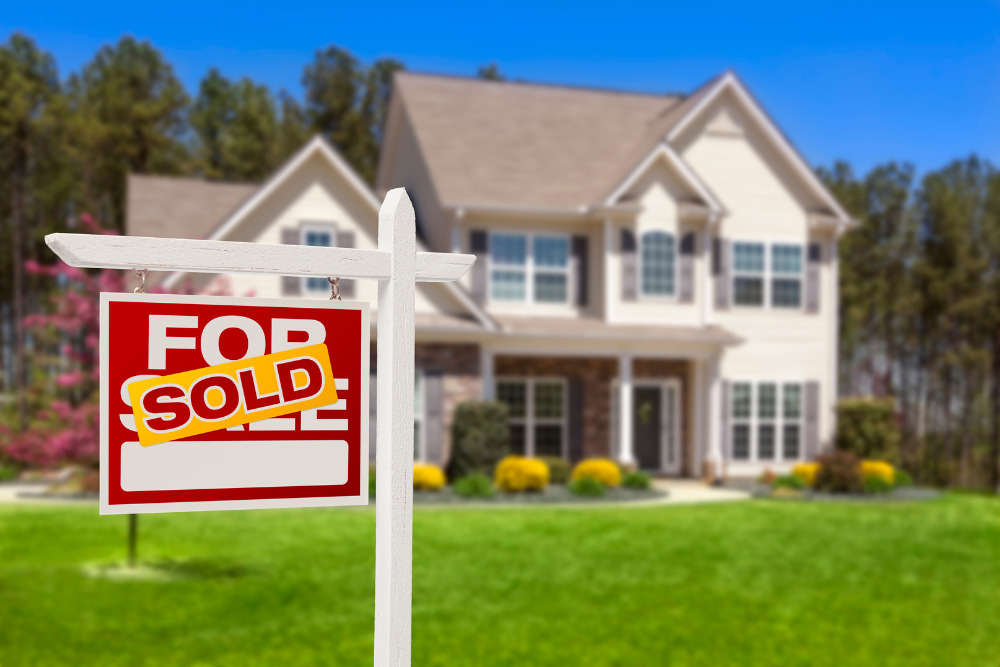
Will Solar Panels Increase The Value Of Your Home?
Solar panels increase the value of your home because future owners will save money in the long run.
According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the value of your home increases by $20 for every dollar that a solar panel saves you on your electrical bill, and Zillow has found that houses with solar panels sell for about 4% higher than houses without them. The exact increase in value would depend on the geographical location of your home, local solar installation prices, system output, and system age of the solar panels.