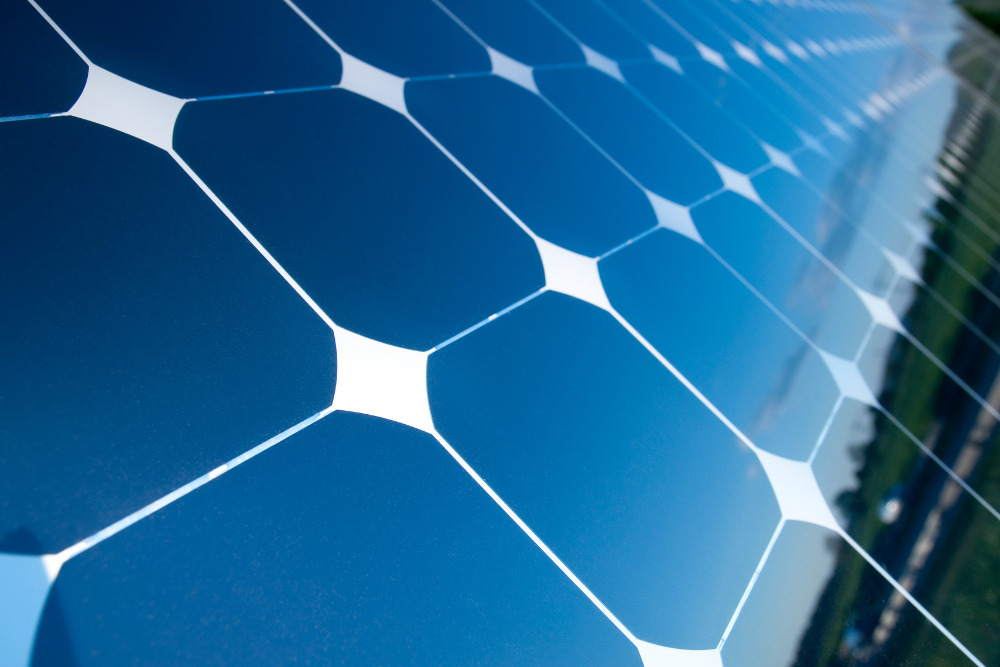
Solar panels come in various types, each with unique features and characteristics. While many newer technologies exist, three types of solar panels are primarily used in mainstream residential and commercial solar installations: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film.
What Are The Three Main Types Of Solar Panels?
The three main types of solar panels utilize specific and different photovoltaic cells (PV cells) and technology. These are monocrystalline solar cells, polycrystalline solar cells (multi-crystalline), and thin-film solar technology.
Each of these has important distinctions that must be understood to choose the optimal solution for your specific energy needs, budget constraints, and installation requirements.
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels. These panels are composed of cells made from silicon wafers with a single crystal structure. They have a uniform black color and are known for their high efficiency. Monocrystalline panels have a higher power output per square foot than other types, making them suitable for limited roof space.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels. These panels are also composed of cells made from silicon wafers. However, they're made of fragmented silicon crystals, which gives them the distinct blue color many solar panels are known for. Their production is faster and cheaper than monocrystalline panels, but they have a lower efficiency rating. That said, polycrystalline panels are a popular choice for homeowners and commercial use due to the balance between cost and performance.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels. Thin-film panels are made by depositing a layer of semiconductor material onto a substrate like glass or plastic. They are lightweight, flexible, and have a lower efficiency compared to crystalline panels. Thin-film panels are often used in large-scale commercial installations where cost-effectiveness and ease of installation are prioritized. Thin-film panels use various elements for the solar cell, including amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS).

It's worth noting that there can be variations and advancements in technology within each of these main types.
What Are The Newest Types Of Solar Panels?
In recent years, the solar industry has witnessed remarkable advancements, leading to the emergence of new and innovative types of solar panels.
- Bifacial Solar Panels. Bifacial panels are capable of capturing sunlight from both the front and back sides. Since the capture sun reflected from the ground, they're ideal in snowy or sandy climates, or when installed over water. Bifacial technology can be integrated with both monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels.
- Perovskite Solar Cells. Perovskite solar cells are thin-film solar cells using a hybrid organic-inorganic lead or tin halide-based material. They have gained attention for their high-efficiency potential and low manufacturing costs. However, they are still in the research and development phase and are not yet widely available.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP). Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) is a renewable energy technology using mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, which converts the sunlight into heat energy. This concentrated heat then generates steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity. CSP systems are often implemented in large-scale power plants in regions with abundant sunlight, such as deserts.
- Organic Solar Cells. Organic solar cells, also known as organic photovoltaics (OPV), are a type of solar technology that utilizes organic materials to convert sunlight into electricity. Unlike traditional silicon solar cells made from pure silicon, organic solar cells are lightweight, and flexible. They can be produced using low-cost manufacturing processes. The organic materials used in these cells are typically carbon-based polymers or small molecules that can absorb photons and generate an electric current. Although organic solar cells have lower efficiency than their pure silicon counterparts, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving their performance and stability, making them a promising avenue for future advancements in solar energy technology.
- Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) panels. PERC panels are a significant advancement. They are designed to increase the efficiency and performance of photovoltaic modules. PERC panels feature a rear passivation layer, typically silicon nitride, that minimizes electron recombination and enhances light absorption, improving energy conversion efficiency.
It's important to note that solar panel technology is constantly evolving, and new advancements may have emerged since this update. The Department of Energy is an excellent source of information regarding the latest developments.
What Is The Best Type Of Solar Panel?
Determining the "best" type of solar panel depends on various factors and individual needs. Different types of solar panels have their own advantages and considerations.
- Efficiency. In a solar panel, efficiency refers to its ability to convert sunlight into electricity. Generally, higher-efficiency panels generate more electricity, which can be beneficial if you have limited space available for installation.
- Cost. The cost of solar panels can vary based on the type and brand. It's essential to consider the upfront cost and any long-term savings and return on investment that the panel may provide.
- Space Availability. The available space for solar panel installation can influence the choice of panel type. You might want to consider higher-efficiency panels to maximize electricity production if you have limited space. Utility-scale solar farms have plenty of space to install slightly less efficient panels to save money.
- Durability and Longevity. The durability and expected lifespan of solar panels are crucial factors to consider. Panels with extended warranties and proven track records of reliability may be preferable.
- Appearance. The visual appearance of solar panels might be a consideration for some individuals. All-black monocrystalline panels with black back sheets create a uniform look, while polycrystalline panels with white back sheets and silver frames create the distinct "waffle" appearance that makes solar panels more noticeable. If you want to camouflage the appearance of your solar panels, SolarSkin overlays can be custom printed to match your roof. Businesses can use the technology to customize their solar array with branding.
- Environmental Impact. Solar panels are already a clean energy source, but some panel types may have lower carbon footprints or less environmental impact during the manufacturing process. It's worth considering the overall environmental impact of the panel technology.
- Climate. The climate is a consideration when choosing the best solar panel for your needs. In areas where sunlight is limited, higher efficiency panels will generate more electricity.
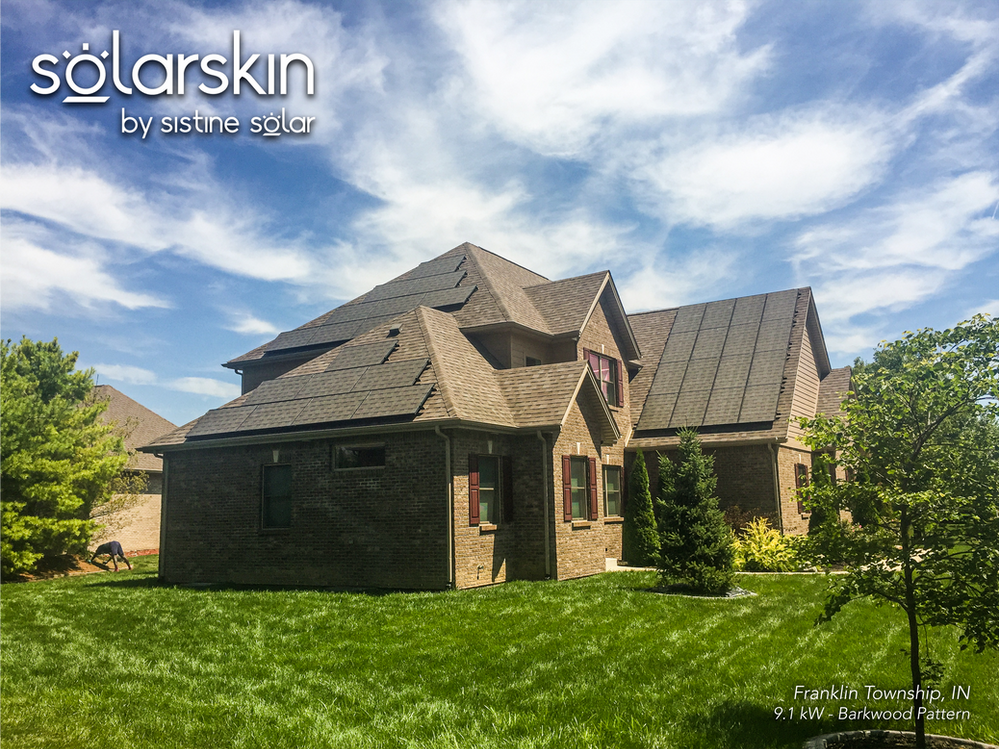

Ultimately, the "best" type of solar panel will depend on your specific circumstances, preferences, and priorities. It's recommended to consult with solar energy professionals and different solar companies and consider factors such as performance, cost, and warranties before deciding.
What Type Of Solar Panel Is Most Efficient?
Currently, the most efficient and widely available solar panel technology is monocrystalline.
With efficiency rates ranging from 18% to 22%, monocrystalline solar panels offer better performance in limited space or where maximizing energy production is a priority. However, it's worth noting that solar panel efficiency can vary depending on factors such as manufacturing technology, materials used, and weather conditions.
What Is The Most Affordable Type Of Solar Panel?
Polycrystalline solar panels are generally considered the most affordable type of solar panels available.
Polycrystalline panels are made from multiple silicon fragments, which are melted together to form the solar cell. This manufacturing process is less expensive compared to the production of monocrystalline panels.
While they have slightly lower efficiency rates than monocrystalline panels, ranging from 15% to 17%, they still offer a cost-effective solution for harnessing solar energy.